Scrubber
A scrubber is a device that cleans flue gas from incinerators or other sources of pollution by using a liquid or solid substance to remove harmful components. Scrubbers can reduce the emissions of acid gases, heavy metals, dust, dioxins and other pollutants that pose a risk to human health or the environment. Scrubbers can be classified into two main types: wet and dry.
Wet scrubbers use water or a chemical solution to spray or wash the flue gas and capture the pollutants. Wet scrubbers can achieve high removal efficiencies for acidic gases, such as sulfur dioxide and hydrogen chloride, as well as particulate matter. However, wet scrubbers also generate wastewater that needs to be treated and disposed of properly.
Dry scrubbers use a dry powder or granular material to react with the flue gas and neutralize the pollutants. Dry scrubbers can be effective for removing heavy metals, mercury and dioxins. Dry scrubbers do not produce wastewater, but they generate solid residues that need to be handled and disposed of safely.
Scrubbers are widely used in various industries, such as power plants, waste incineration, chemical production, metal smelting and refining. Scrubbers are designed to meet the specific requirements of each application, such as the type and quantity of the waste, the composition and temperature of the flue gas, and the environmental standards and regulations.
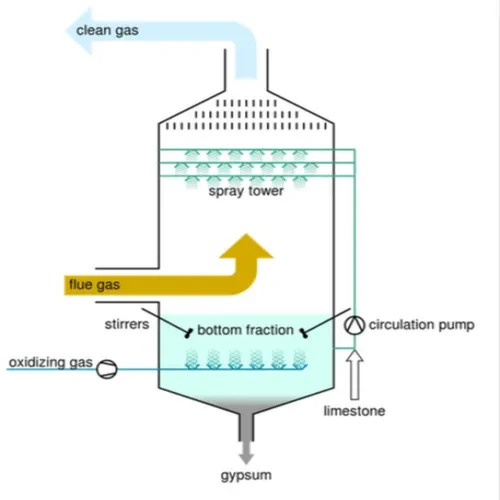
-
Cleaning efficiency 70% of fine dust and 80% of coarse dirt
-
Air velocity 2 - 3m/s
-
Pressure drop 50 - 140N/m2
-
Water pressure 100 - 170kN/m2
-
Water consumption 0.45 - 0.55 l/m3 air
-
Scrubber type Wet or dry, packed bed or venturi
-
Pollutants scrubbed Acid gases, heavy metals, dust, dioxins
Start your free consultation
Let’s assess your needs, analyse your current proccesses and see how Cybertig can implement the change that your organisation requires. We’re here to help.
